Complex target mappings (PowerShell v2 target systems)
HelloID supports JavaScript for complex mappings. Use them to transform or format mapped user attributes using custom JavaScript code. Complex mappings support the ECMAScript 5.1 standard.
Use the Person object to access fields in the current person. The properties of this object correspond to the fields in the Person schema, including the Special fields (such as the person's contracts, and any custom fields). For example, a person's first name may be available at Person.Name.GivenName. Do not attempt to initialize or overwrite these properties.
Use the Person.Accounts. object to Use shared fields in PowerShell v2 via the Share account fields between target systems feature. For example, Person.Accounts.AzureAD.Title. Do not attempt to initialize or overwrite these properties.
Complex target mappings support several types of Uniqueness checks, using the Iteration variable.
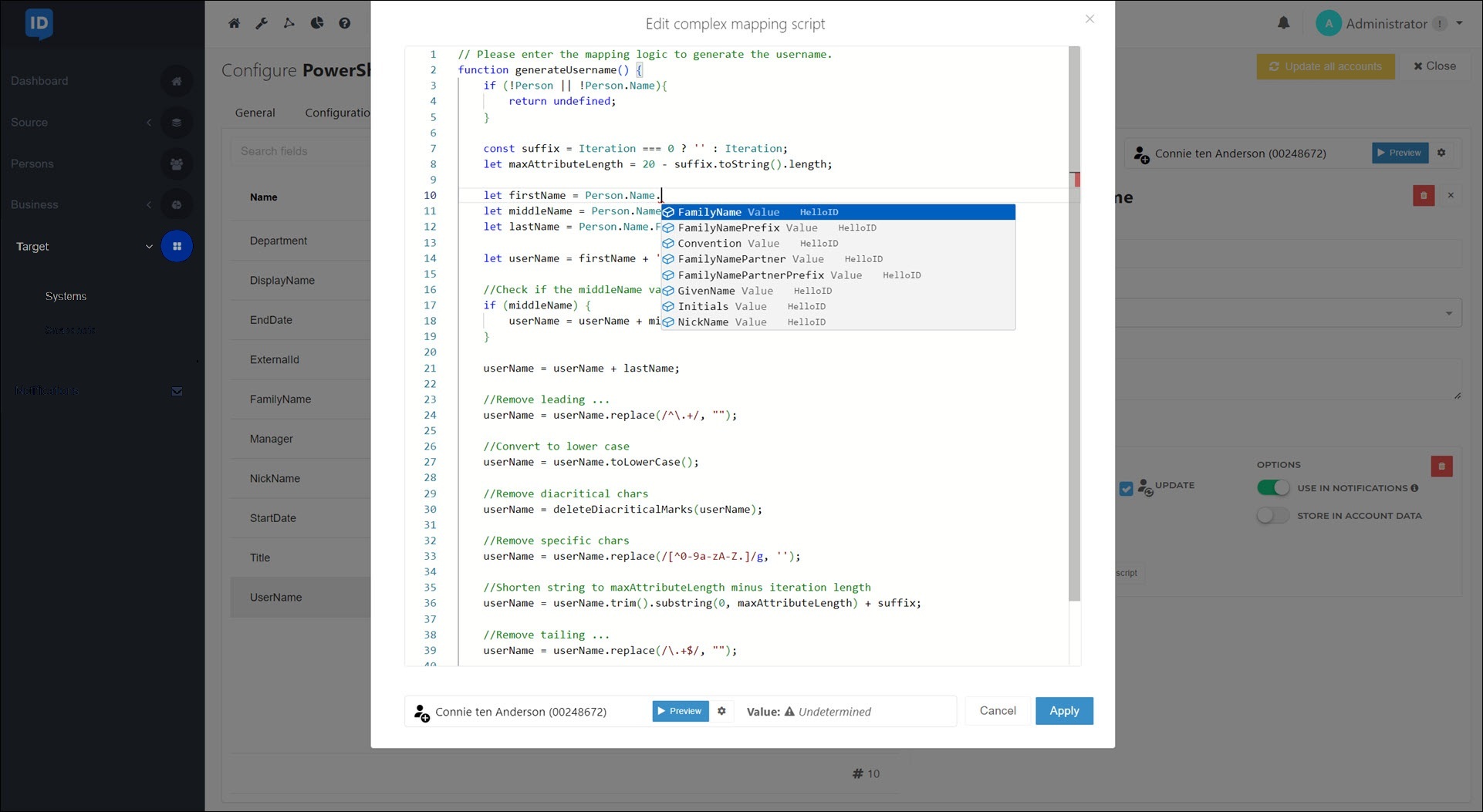
In PowerShell v2 systems, complex mappings support both autocomplete and preview.
Tip
Ready-made functions for a number of frequently used complex mappings can be found in Tools4ever's GitHub resources: Target JavaScript functions.
The following script is an example of a complex target mapping.
// Please enter the mapping logic to generate the username.
function generateUsername() {
if (!Person || !Person.Name){
return undefined;
}
const suffix = Iteration === 0 ? '' : Iteration;
let maxAttributeLength = 20 - suffix.toString().length;
let firstName = Person.Name.NickName;
let middleName = Person.Name.FamilyNamePrefix;
let lastName = Person.Name.FamilyName;
let userName = firstName + '.';
//Check if the middleName variable contains data
if (middleName) {
userName = userName + middleName.replace(/\s+/g, '.') + '.';
}
userName = userName + lastName;
//Remove leading ...
userName = userName.replace(/^\.+/, "");
//Convert to lower case
userName = userName.toLowerCase();
//Remove diacritical chars
userName = deleteDiacriticalMarks(userName);
//Remove specific chars
userName = userName.replace(/[^0-9a-zA-Z.]/g, '');
//Shorten string to maxAttributeLength minus iteration length
userName = userName.trim().substring(0, maxAttributeLength) + suffix;
//Remove tailing ...
userName = userName.replace(/\.+$/, "");
return userName;
}
generateUsername(); The following script is an example of a complex target mapping that calculates an employee’s FTE percentage by adding the FTE values of all their active contracts.
function getFtePercentage() {
let value = null
for (let i = 0; i < Person.Contracts.count; i++) {
if(Person.Contracts[i].Context.InConditions) {
value = value + Person.Contracts[i].Details.fte
}
}
return (value * 100).toFixed(2)
}
getFtePercentage();